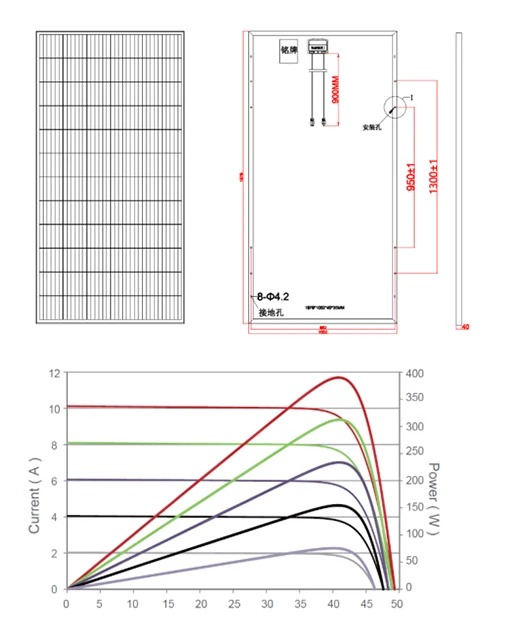
Electrolytic Cells: A Buyer's Guide for Industrial Machinery in 2025
In the rapidly evolving industrial sector, electrolytic cells play a crucial role in various applications, from metal refining to chemical production. As we approach 2025, sourcing reliable and high-performance electrolytic cells from China has become a priority for many businesses. This guide will help you navigate the market and make informed decisions.
How to Find Reliable Electrolytic Cells from China in 2025
China remains a global leader in manufacturing industrial machinery, including electrolytic cells. To find reliable suppliers, consider these steps:
- Check certifications like ISO 9001 and CE
- Review supplier history and customer feedback
- Request product samples before bulk orders
- Verify production capacity and lead times
Top platforms like Alibaba and Made-in-China list reputable manufacturers with verified track records.
What Buyers Should Know Before Buying Electrolytic Cells from China
When importing electrolytic cells, consider:
- Shipping costs and import duties
- Voltage compatibility with your local grid
- After-sales support and warranty terms
- Customization options available
Always request detailed product specifications and confirm they meet your operational requirements.
Types of Electrolytic Cells
Common electrolytic cell types include:
- Diaphragm cells: For chlorine and caustic soda production
- Membrane cells: Higher efficiency for chemical processes
- Mercury cells: Used in chlor-alkali processes (being phased out)
- Solid oxide cells: For high-temperature applications
Functions and features of Electrolytic Cells
Modern electrolytic cells offer:
- Energy-efficient designs reducing operational costs
- Corrosion-resistant materials for longer lifespan
- Precision control systems for consistent output
- Modular designs for easy maintenance
Advanced models may include automated monitoring and smart control features.
Scenarios of Electrolytic Cells
Electrolytic cells are essential in:
- Metal extraction and refining (aluminum, copper, zinc)
- Water treatment and purification systems
- Chemical manufacturing (chlorine, sodium hydroxide)
- Battery and energy storage technologies
How to Choose Electrolytic Cells
Selecting the right electrolytic cell depends on:
- Your specific industrial application
- Required production capacity
- Available space and installation requirements
- Budget and long-term operational costs
Consult with technical experts to match the cell specifications with your process needs.
Electrolytic Cells Q & A
Q: What's the typical lifespan of industrial electrolytic cells?
A: Quality cells last 5-8 years with proper maintenance, though membranes may need replacement sooner.
Q: How much energy do electrolytic cells consume?
A: Consumption varies by type, with modern membrane cells using 2,200-2,500 kWh per ton of product.
Q: Can electrolytic cells be customized for specific processes?
A: Yes, many Chinese manufacturers offer customization for electrode materials, cell size, and control systems.
Q: What safety features should I look for?
A: Prioritize cells with temperature controls, pressure relief systems, and leak detection.
Q: How do I maintain electrolytic cells?
A: Regular cleaning, membrane inspection, and electrolyte monitoring are essential for optimal performance.